What Is Unearned Revenue? A Definition and Examples for Small Businesses

In accounting, unearned revenue is prepaid revenue. This is money paid to a business in advance, before it actually provides goods or services to a client. Unearned revenue is a liability, or money a company owes. When the goods or services are provided, an adjusting entry is made. Unearned revenue is helpful to cash flow, according to Accounting Coach.
In this article, we’ll cover:

What Is Unearned Revenue?
Unearned revenue is an account in financial accounting. It’s considered a liability, or an amount a business owes. It’s categorized as a current liability on a business’s balance sheet, a common financial statement in accounting.
Small businesses receive unearned revenue when a client pays for goods or services before the business sends the goods or performs the service. It’s also known as “prepaid revenue.”
Examples of unearned revenue include:
- Service contract paid in advance
- Legal retainer paid in advance
- Advance rent payment
- Prepaid insurance
Unearned Revenue in the Books
When the business provides the good or service, the unearned revenue account is decreased with a debit and the revenue account is increased with a credit.
If a business entered unearned revenue as an asset instead of a liability, then its total profit would be overstated in this accounting period. The accounting period were the revenue is actually earned will then be understated in terms of profit.
Not entering revenue received in the same period as expenses paid for a project also violates the matching principle of accounting that says revenue and expenses for the same project must be “matched.”
The Importance of Unearned Revenue
Unearned revenue is great for a small business’s cash flow as the business now has the cash required to pay for any expenses related to the project in the future, according to Accounting Tools.
What Is an Unearned Revenue Example?
Example #1
A client buys a dog walking package in advance. The package is for three month’s worth of walks. At $400 per month, the cost is $1200. The client pays $1200 upfront. The business owner enters $1200 as a debit to cash and $1200 as a credit to unearned revenue.
The owner then decides to record the accrued revenue earned on a monthly basis. The earned revenue is recognized with an adjusting journal entry called an accrual.
At the end of the month, the owner debits unearned revenue $400 and credits revenue $400. He does so until the three months is up and he’s accounted for the entire $1200 in income both collected and earned out.
Example #2
A client purchases a package of 20 person training sessions for $2000, or $100 per session. She pays for them in advance. The personal trainers enters $2000 as a debit to cash and $2000 as a credit to unearned revenue.
The client doesn’t have regular training sessions. After two months, she attends five personal training session. This means she’s done 25 percent of her 20 pre-paid sessions. So, the trainer can recognize 25 percent of unearned revenue in the books, or $500 worth of sessions. She debit unearned revenue $500 and credits revenue $500.
People also ask:
- What Is Unearned Revenue on a Balance Sheet?
- What Is the Journal Entry for Unearned Revenue?
- What Is Unearned Revenue vs. Deferred Revenue?
What Is Unearned Revenue on a Balance Sheet?
Unearned revenue is reported on a business’s balance sheet, an important financial statement usually generated with accounting software.
Here’s an example of a balance sheet. Unearned revenue is not a line item on this balance sheet. It would go in the “liabilities” category, as it is money owing. The business has not yet performed the service or sent the products paid for.
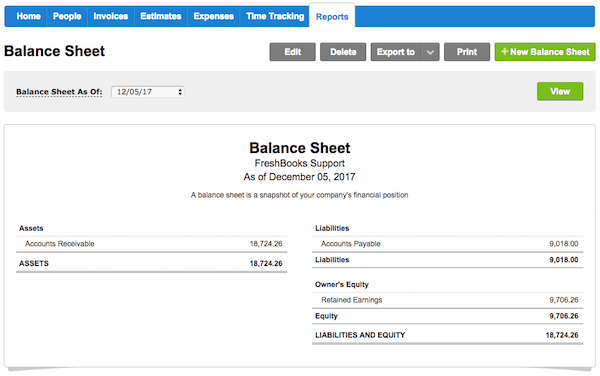
Source: FreshBooks
The below example shows a more detailed balance sheet. Unearned revenue is listed under “current liabilities.” It is part of the total current liabilities as well as total liabilities.
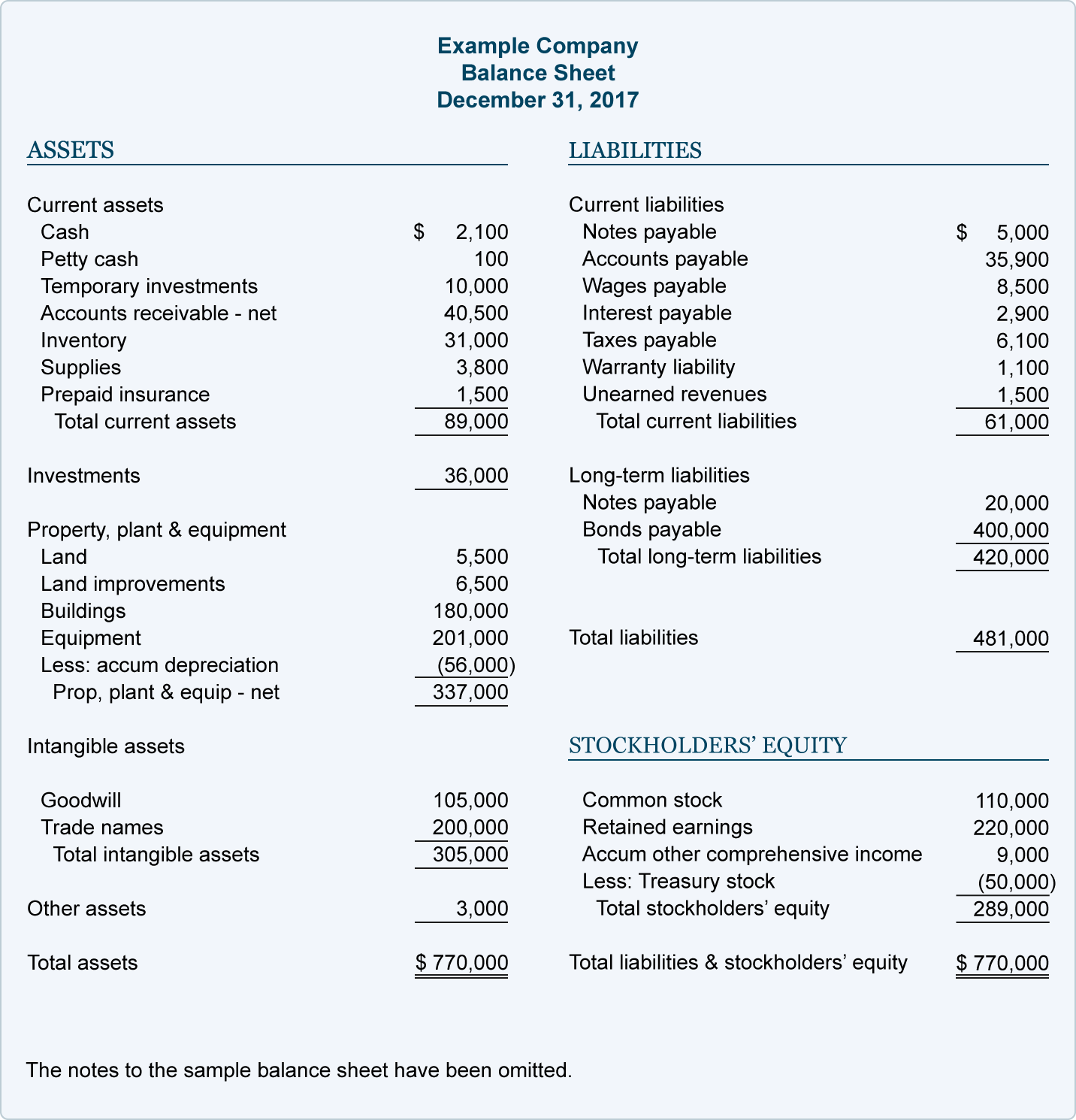
On a balance sheet, assets must always equal equity plus liabilities. Both sides of the equation must balance.
This is why unearned revenue is recorded as an equal decrease in unearned revenue (a liability account) and increase in revenue (an asset account). This makes sure the equation continues to balance.
FreshBooks has online accounting software for small businesses that makes it easy to generate balance sheets and view your unearned revenue.

What Is the Journal Entry for Unearned Revenue?
Unearned revenue is originally entered in the books as a debit to the cash account and a credit to the unearned revenue account.
The credit and debit are the same amount, as is standard in double-entry bookkeeping. Also, each transaction is always recorded in two accounts.
This journal entry reflects the fact that the business has an influx of cash but that cash has been earned on credit. It is a pre-payment on goods to be delivered or services provided.
Once the business actually provides the goods or services, an adjusting entry is made. The unearned revenue account will be debited and the service revenues account will be credited the same amount, according to Accounting Coach.
This means that two journal entries are made for unearned revenue: when it’s received and when it’s earned.
- For example, a contractor quotes a client $1000 to retile a shower. The client gives the contractor a $500 prepayment before any work is done. The contractor debits the cash account $500 and credits the unearned revenue account $500. Later, the contractor finishes half the job. He makes an adjusting entry where he debits the unearned revenue account $500 and credits the service revenues account $500.
What Is Unearned Revenue vs. Deferred Revenue?
Unearned revenue and deferred revenue are two ways of referring to the same idea: revenue that has been received but has not yet been earned. Deferred revenue is also called deferred income.
Both these terms refer to advances from customers. Since the actual goods or services haven’t yet been provided, they are considered liabilities, according to Accountingverse.
RELATED ARTICLES
 W-8BEN-E: Guide for Foreign Entities Doing Business in the U.S.
W-8BEN-E: Guide for Foreign Entities Doing Business in the U.S. Accounting for Sales Tax: What Is Sales Tax and How to Account for It
Accounting for Sales Tax: What Is Sales Tax and How to Account for It Business Deductions for the Self-Employed: 12 Overlooked Tax Deduction Tips
Business Deductions for the Self-Employed: 12 Overlooked Tax Deduction Tips Billable Hours: What Are They and How to Calculate Them
Billable Hours: What Are They and How to Calculate Them Is Land a Current or Long-Term Asset? How to Classify Land on the Balance Sheet
Is Land a Current or Long-Term Asset? How to Classify Land on the Balance Sheet Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable: What’s the Difference?
Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable: What’s the Difference?