What Is an Acid Test Ratio?

An acid ratio test, also known as a quick ratio, measures the ability of a company to use their short-term assets to cover their immediate liabilities. The number will be stronger than the current ratio since it ignores assets such as inventory.
A normal liquid ratio is considered to be 1:1. If a company has a ratio of less than 1, they cannot currently fully pay back its current liabilities. Having a quick ratio of 2.0 means that you have $2.00 in liquid assets available to cover each $1.00 of current liabilities.
To understand a company’s current liquid assets, we add cash and cash equivalents, short-term marketable securities, accounts receivable and vendor non-trade receivables. Then divide current liquid assets by total current liabilities to calculate the acid test ratio.
The formula to calculate the acid test ratio is:
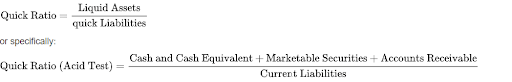
This article will also discuss:
Is a High Acid Test Ratio Good?
How Can I Improve My Acid Test Ratio?
How Do You Read the Acid Test Ratio?

Is a High Acid Test Ratio Good?
A low or decreasing acid test ratio generally suggests that a company is struggling to maintain or grow sales, paying their bills too quickly, collecting receivables too slowly or over-leveraged.
On the other hand, a high or increasing acid test ratio indicates a company has faster inventory turnover and cash conversion cycles. This ratio happens when a company is experiencing top-line growth, quickly converting receivables into cash, and are easily able to cover its financial obligations.
How Can I Improve My Acid Test Ratio?
Companies with higher acid test ratios are considered to be more financially stable than those with a lower quick ratio. An acid test ration greater than 1 is considered healthy and is important for external stakeholders like creditors, lenders, investors and capitalists.
Here are three ways to improve a company’s acid test ratio:
1) Pay Off Liabilities Quickly
An essential method to improve your acid test ratio is to keep the company’s liabilities under control. In the acid test ratio, current liabilities are in the denominator that if kept low will put your business in a better position. This can be done through paying off creditor quickly and reducing the repayment terms on your loans.
2) Increase Inventory Turnover & Sales
Increasing your sales will improve your inventory turnover which can increase a company’s cash on hand. Increased sales and inventory turnover mean more cash will be available to the company to meet their short-term obligations. In order for inventory to be converted into cash, it must be actively sold. Increased sales that turnover your inventory will improve your acid ratio test.
3) Reduce Invoice Collection Period
Decreasing time period for the collection of your accounts receivable will have a direct and positive impact on your business’ acid ratio test.
A shorter collection period can help a company’s incoming cash flow and reduce the chances of encountering long-term debtors, sticky debtors and bad debts. Make your invoice terms clear in the beginning of the transaction to ensure the liquidity of your accounts receivable. Also, ensure active collection efforts.

How Do You Read the Acid Test Ratio?
If your acid test ratio is less than 1, your company does not have enough liquid assets to pay their current liabilities.
Acid test ratios that are much lower than the current ratio means that current assets are highly dependent on inventory. This is not always a bad sign, as some business models are dependent on inventory. Retail stores might have a very low acid test ratio without necessarily being in financial danger. In these cases, other metrics should be considered such as inventory turnover.
An acceptable acid test ratio range will vary by industry.
Most industries should have acid test ratios that exceed 1. Although very high ratios are not a positive thing. High acid test ratios could indicate that cash has accumulated rather than being reinvested, returned to stakeholder or put to productive use.
RELATED ARTICLES
 How to Choose the Right Accounting Software for Your Business?
How to Choose the Right Accounting Software for Your Business? Accounting Changes & Corrections 101
Accounting Changes & Corrections 101 What Is the Installment Method? | Accounting Definitions and Examples
What Is the Installment Method? | Accounting Definitions and Examples How Purchase Orders Work. How This Important Document Helps Businesses.
How Purchase Orders Work. How This Important Document Helps Businesses. Do I Need an Accountant for My Small Business?
Do I Need an Accountant for My Small Business? What Are Functional Expenses? A Guide to Nonprofit Accounting
What Are Functional Expenses? A Guide to Nonprofit Accounting